Casting parts of machine tool - HT200
Casting parts of machine tool - HT200
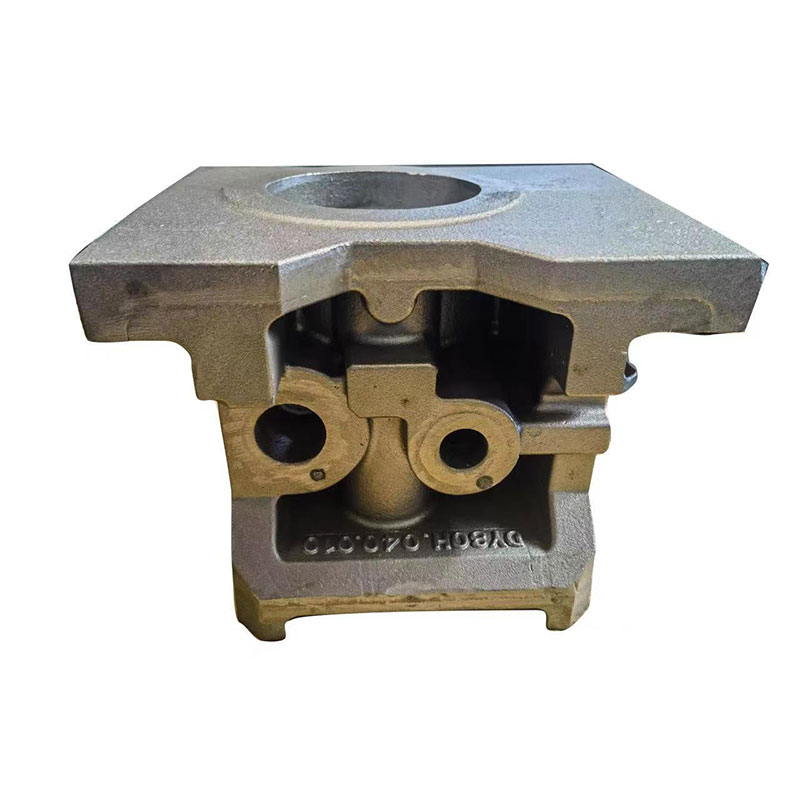

Material No.:HT200
Processing technology: Investment casting CNC machining
Casting parts of machine tool are an important component in the manufacturing process of machine tools. They are used to create the structure and framework of the machine tool, and are typically made from materials such as iron, steel, or aluminum. The casting process involves pouring molten metal into a mold, which is then allowed to cool and solidify into the desired shape. The resulting casting is then machined and finished to the required specifications.

What materials are commonly used for casting machine tool parts?
There are several materials commonly used for casting machine tool parts. These materials are selected based on the specific requirements of the machine tool and the desired characteristics of the parts. Some common materials include:
1. Cast Iron: Cast iron is widely used in machine tool casting due to its high strength, wear resistance, and ability to dampen vibrations. It provides stability and rigidity to the machine tool parts, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2. Steel: Different types of steel, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, can be used for machine tool casting. Steel offers a good balance between strength, toughness, and machinability.
3. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys: Aluminum is used in machine tool casting when lighter weight is desired. It provides good thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and lower machining costs. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, are commonly used due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
4. Brass and Bronze: These copper-based alloys are used for machine tool casting when good corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and low friction are required.
5. Zinc: Zinc casting is utilized for smaller machine tool parts or complex shapes that require a high level of intricacy and precision.
6. Polymer/Plastic: In some cases, polymer or plastic materials, such as nylon or polyethylene, are used for machine tool casting when low weight, low cost, and insulation properties are required. However, plastic casting is more commonly used in low-load or non-structural parts.
It is essential to choose the appropriate material based on factors like mechanical requirements, environmental conditions, and cost considerations to ensure efficient performance and longevity of machine tool parts.